Exploring Hydroponics: Understanding Different Systems
Hydroponics is an exciting method of growing plants without soil. Have you ever wondered how it works? In this article, we’ll dive into the fascinating world of hydroponic systems and explore the different types available. Get ready to uncover the secrets behind this innovative approach to gardening!
When it comes to hydroponic systems, there’s no one-size-fits-all solution. Each type has its own unique features and benefits. Whether you’re a gardening enthusiast or just curious about modern farming techniques, understanding the various hydroponic systems is a stepping stone towards becoming a green-thumb expert.
From the simplicity of the wick system to the precision of the nutrient film technique, there’s a hydroponic system to suit every level of expertise. Each system has its pros and cons, ensuring that you can find the perfect fit for your gardening goals. So, let’s embark on this hydroponic journey and explore the diverse world of hydroponic systems together!

Types of Hydroponic Systems: A Comprehensive Guide
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on the different types of hydroponic systems. If you’re new to hydroponics or looking to expand your knowledge, you’ve come to the right place. In this article, we’ll explore seven popular hydroponic systems, discussing their benefits, drawbacks, and how they work. Whether you’re a hobbyist or a professional grower, understanding the various hydroponic systems available will help you make informed decisions and achieve success in your endeavors. Let’s dive in!
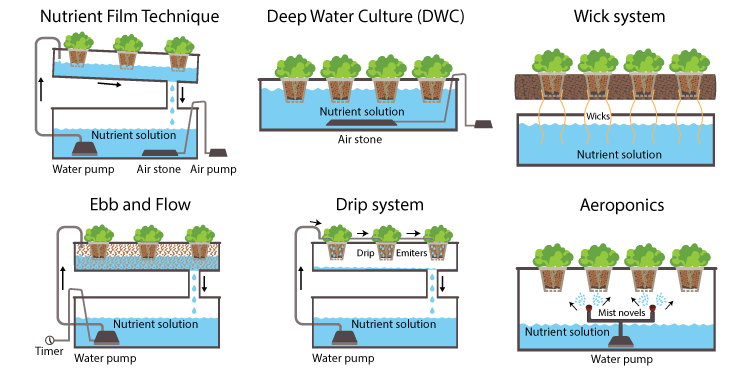
Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) System
The Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) system is one of the most popular hydroponic systems due to its simplicity and efficiency. In an NFT system, a thin film of nutrient-rich water is continuously circulated over the roots of the plants, providing essential nutrients and oxygen. This system uses a slope or channel to allow gravity to assist with the flow of the nutrient solution. The roots are exposed to a thin film of nutrient solution, allowing them to absorb what they need before the excess returns to the reservoir.
NFT systems require precise control of the nutrient solution flow, as too little or too much can negatively affect plant growth. However, they offer several advantages. NFT systems are highly water-efficient, as they require less water compared to traditional soil-based farming. They also allow for faster growth and higher yields, as the continuous flow of nutrients and oxygen promotes healthy root development. Additionally, NFT systems are easily scalable, making them suitable for a range of applications, from small home setups to large commercial operations.
When using an NFT system, it’s important to closely monitor and maintain the nutrient solution’s pH and nutrient levels. Regular cleaning and inspection of the channels or slopes are also necessary to prevent clogs or blockages. Overall, the NFT system is an excellent choice for growers looking for a low-maintenance, water-efficient, and high-yielding hydroponic system.
Deep Water Culture (DWC) System
The Deep Water Culture (DWC) system is another popular choice among hydroponic growers. This system involves suspending plant roots in a nutrient-rich solution with the use of net pots or foam boards. The roots remain submerged in the solution, allowing them to draw nutrients directly from the water. Oxygen is supplied through air stones or diffusers, which create bubbles and keep the nutrient solution aerated. The continuous circulation of oxygenated water ensures that the roots receive a constant supply of oxygen.
The DWC system offers several advantages. First, it provides a high level of oxygenation to the roots, promoting healthy and robust plant growth. This system is also relatively simple and easy to set up, making it suitable for beginners. Additionally, the DWC system requires minimal water and nutrient usage, contributing to its cost-effectiveness.
However, the DWC system also has some considerations. Regular monitoring of the nutrient solution’s pH and oxygen levels is crucial for maintaining optimal plant health. As the roots are constantly in contact with the nutrient solution, any imbalances or fluctuations can quickly impact the plants. Additionally, the DWC system may not be suitable for larger plants with extensive root systems, as the floating roots may become entangled. Overall, the DWC system is an excellent choice for growers looking for a low-cost and efficient hydroponic system.
Aeroponics System
The Aeroponics system takes hydroponics to a whole new level by suspending plant roots in the air and misting them with a nutrient-rich solution. This system relies on the precise delivery of a fine mist of water and nutrients to the roots, providing them with optimal moisture and oxygen. The suspended roots are able to absorb the nutrients directly from the mist.
Aeroponics systems offer numerous advantages. Firstly, they provide excellent oxygenation to the roots, promoting rapid and healthy plant growth. The high oxygen levels in the root zone also enhance nutrient uptake and contribute to faster growth rates and higher yields. Additionally, aeroponics systems are highly water-efficient, as they use minimal water compared to traditional soil-based agriculture.
However, the complexity and maintenance requirements of aeroponics systems may pose challenges for beginners or casual growers. The precise control and monitoring of the nutrient mist, along with regular maintenance of the misting nozzles, can be time-consuming. Any clogs or malfunctions in the misting system can quickly affect plant health. It’s also important to note that aeroponics systems are more sensitive to power outages or disruptions, as the suspended roots rely entirely on the mist for their nourishment.
Types of Hydroponic Systems Continued:
Ebb and Flow (Flood and Drain) System
The Ebb and Flow system, also known as the Flood and Drain system, is a versatile and popular choice among hydroponic growers. This system involves periodically flooding the plant roots with a nutrient solution, which then drains away, allowing the roots to access air. The flooding and draining cycles are controlled by a timer or a hydroponic pump.
Ebb and Flow systems offer several benefits. They provide a constant supply of nutrients and oxygen to the roots, fostering healthy growth and optimum nutrient uptake. The periodic flooding and draining cycles also help prevent the buildup of stagnant water and potential root rot. Additionally, Ebb and Flow systems are highly adaptable and can accommodate a wide range of plant sizes and types.
However, Ebb and Flow systems require careful monitoring of the nutrient solution’s pH and water levels to ensure they’re within the optimal range. It’s also important to regularly inspect and maintain the drainage system to prevent clogs or blockages. Improper drainage can lead to waterlogging and suffocate the roots. Despite these considerations, the Ebb and Flow system remains a popular choice due to its flexibility, ease of use, and ability to support a variety of plant species.
Wick System
The Wick system is one of the simplest and most affordable hydroponic systems available. This passive system operates by drawing nutrient-rich water from a reservoir up into the growing medium via a wick. The growing medium, typically coconut coir or perlite, acts as a wick, carrying the water and nutrients to the plant roots.
The Wick system offers several advantages. It requires no electricity or complex equipment, making it accessible to beginners or growers with limited resources. The system is also easy to set up and low maintenance. Additionally, the Wick system is ideal for smaller plants or herbs with shallow root systems.
However, the Wick system may not be suitable for larger or more demanding plants, as the wick may struggle to provide sufficient water and nutrients. The system also relies on capillary action, which can be slow. It’s important to choose an appropriate wick material with good water absorption properties. Despite its limitations, the Wick system serves as an excellent introduction to hydroponics and is a cost-effective option for small-scale growers.
Drip System
The Drip system, also known as the Recovery or Non-Recovery system, is a widely used method that involves providing a controlled and regular supply of nutrient solution to the plant roots using a network of tubes or emitters. The nutrient solution is delivered in the form of drips or drops onto the growing medium or root zone.
Drip systems offer numerous advantages. They allow for precise control over the nutrient solution delivery, ensuring that plants receive the optimal amount of water and nutrients. The slow and steady dripping also helps maintain the moisture balance in the growing medium. Additionally, drip systems are suitable for a wide range of plants and can be easily customized depending on the specific requirements.
However, drip systems can be more complex to set up and may require more upfront investment compared to some other hydroponic systems. Constant monitoring and regular inspection of the emitters are necessary to prevent clogs or malfunctions. It’s also important to consider the proper disposal or recycling of the runoff nutrient solution in non-recovery systems. Despite these considerations, drip systems are highly versatile and efficient, making them a popular choice for both small-scale and large-scale hydroponic operations.
Vertical Tower System
The Vertical Tower system, also known as the Vertical Farm or Tower Garden, is an innovative and space-saving hydroponic system. As the name suggests, this system involves cultivating plants in vertically stacked layers or towers. Each level contains multiple planting pockets or containers, allowing for high plant density.
The Vertical Tower system offers several advantages, making it increasingly popular for urban gardening and limited-space environments. It maximizes vertical growing space, making it ideal for balconies, rooftops, or indoor settings where horizontal space is limited. The system also allows for efficient use of water and nutrients, as the excess from one level can be collected and reused on the lower levels.
However, the Vertical Tower system may require more upfront investment due to the cost of the vertical structures and supporting equipment. Adequate lighting, ventilation, and irrigation systems are crucial for the successful operation of vertical farms. Additionally, the positioning of the tower and rotation of the plants may require regular adjustments to ensure sunlight is evenly distributed. Despite these considerations, the Vertical Tower system offers an innovative and space-efficient solution for urban gardening and maximizing crop production.
Benefits of Hydroponic Systems
Hydroponic systems offer numerous benefits over traditional soil-based agriculture. Here are some key advantages:
- Water Efficiency: Hydroponic systems use up to 90% less water compared to traditional farming methods.
- No Soil Limitations: Hydroponics allows plants to grow in a controlled environment without the need for fertile soil, making it suitable for any location.
- Faster Growth and Higher Yields: The optimized nutrient delivery in hydroponic systems promotes faster growth and increased crop yields.
- Year-Round Cultivation: Hydroponics enables year-round cultivation, eliminating seasonality constraints.
- Pest and Disease Control: The absence of soil minimizes the risk of pests and diseases, reducing the need for chemicals.
- Space Efficiency: Hydroponic systems can be designed to maximize vertical space, making them ideal for urban gardening and small-scale setups.
Hydroponic Systems vs. Traditional Soil-Based Agriculture
Let’s compare hydroponic systems with traditional soil-based agriculture to understand their differences and advantages:
| Hydroponic Systems | Traditional Soil-Based Agriculture | |
|---|---|---|
| Water Usage | Significantly less water usage | Higher water consumption |
| Space Efficiency | Maximizes vertical space | Dependent on horizontal land availability |
| Pest and Disease Control | Minimized risk of pests and diseases | Prone to pests and diseases |
| Nutrient Control | Precise control over nutrient delivery | Reliant on soil fertility and composition |
| Year-Round Cultivation | Possible with proper environmental controls | Seasonality constraints |
Tips for Success with Hydroponic Systems
While hydroponic systems offer many advantages, success relies on careful planning and proper implementation. Here are some tips to help you achieve optimal results:
- Invest in quality equipment and materials.
- Monitor and maintain appropriate pH levels and nutrient concentrations.
- Regularly inspect and clean system components to prevent clogs or blockages.
- Ensure proper lighting, ventilation, and temperature control.
- Be mindful of plant spacing and avoid overcrowding.
- Follow a regular maintenance schedule to keep your system running smoothly.
Conclusion
Hydroponic systems offer a wide range of options for growers, from small-scale setups to large commercial operations. Understanding the different types of hydroponic systems and their benefits allows you to choose the most suitable system for your needs. Whether you opt for a Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) system, a Deep Water Culture (DWC) system, or any other system, the key is to maintain precise control over the nutrient solution, light, temperature, and airflow. With proper care and attention, hydroponic systems can provide sustainable and efficient cultivation methods that enable year-round production and higher yields. Happy growing!
Key Takeaways: Types of Hydroponic Systems
In hydroponics, there are different types of systems you can choose from.
- Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) – Plants are grown in a shallow, sloping trough where a thin film of nutrient-rich water flows over their roots.
- Deep Water Culture (DWC) – Plants are partially or fully submerged in a nutrient solution, with an air pump providing oxygen to the roots.
- Drip System – Nutrient solution is dripped slowly onto the base of each plant, delivering water and nutrients directly to the root zone.
- Aeroponics – Plants are suspended in air and nutrient-rich mist is sprayed directly onto their roots.
- Vertical Farming – Plants are stacked in vertical layers, using less space and optimizing growth with artificial lighting.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some commonly asked questions about hydroponic systems and their different types:
1. What are the different types of hydroponic systems?
There are several types of hydroponic systems, each with its own unique method of delivering nutrients to the plants. Some common types include:
The first type is the nutrient film technique (NFT), where a shallow stream of nutrient-rich water is continuously circulated over the roots. Another type is the deep water culture (DWC) system, where the roots are suspended in nutrient-rich water. The ebb and flow system (also known as flood and drain) intermittently floods the plants with nutrient solution and then drains it. Additionally, there are aeroponic systems, which mist the roots with a nutrient solution, and the drip system, which delivers a slow, steady drip of nutrient solution to the plants.
2. Which hydroponic system is best for beginners?
For beginners, a simple and easy-to-set-up hydroponic system like the deep water culture (DWC) system is recommended. The DWC system involves suspending the roots in nutrient-rich water with an oxygenating system. This system is relatively low-maintenance and allows beginners to learn the basics of hydroponic gardening.
Another beginner-friendly option is the drip system, which delivers a slow and precise drip of nutrient solution to plants. It is a versatile system that can be used for various types of plants and is customizable to fit different sizes of growing spaces.
3. Which hydroponic system is best for large-scale commercial farming?
For large-scale commercial farming, the nutrient film technique (NFT) system is often preferred. This system allows for high-density planting and efficient use of space. The NFT system involves a constant flow of nutrient-rich water over the roots, providing a continuous supply of nutrients to the plants. It is commonly used for growing lettuce, herbs, and other leafy greens on a large scale.
Another system commonly used in large-scale farming is the aeroponic system. This system mists the roots with a nutrient solution, providing efficient nutrient uptake and oxygenation. It allows for precise control over the growing environment, making it suitable for crops like tomatoes and strawberries.
4. Can hydroponic systems be used for growing vegetables and fruits?
Absolutely! Hydroponic systems can be used to grow a wide variety of vegetables and fruits. In fact, hydroponic gardening can often result in higher yields and faster growth compared to traditional soil-based gardening. Leafy greens like lettuce and herbs are commonly grown using hydroponic systems. Tomatoes, cucumbers, peppers, strawberries, and even melons can also be successfully grown in hydroponic setups.
By providing a controlled environment with the right balance of nutrients, oxygen, and water, hydroponic systems can produce high-quality, flavorful fruits and vegetables.
5. Are hydroponic systems more environmentally friendly than traditional farming?
Hydroponic systems have several environmental benefits compared to traditional farming methods. First, hydroponic systems use significantly less water. This is because the water in hydroponic systems is recirculated, reducing water waste. Additionally, using hydroponic systems eliminates the need for soil, reducing soil erosion and the use of harmful pesticides and herbicides.
Furthermore, hydroponic systems can be set up in urban areas and vertical farms, reducing the need for transportation and minimizing the carbon footprint associated with long-distance food transportation. Overall, hydroponic systems have the potential to be more sustainable and environmentally friendly when compared to traditional farming.
Summary
Hydroponic systems are a cool way to grow plants without soil. There are different types of hydroponic systems, like the drip system and the nutrient film technique. Each system has its own way of delivering water and nutrients to the plants. The floating raft system uses a floating platform to support the plants. The ebb and flow system floods the plants with water and then drains it away. The aeroponic system sprays a mist of water and nutrients onto the plant’s roots. No matter which system you choose, hydroponics is a clever way to grow plants!
In hydroponics, you can grow plants in a controlled environment without worrying about soil quality. It’s a fun and interesting way to learn about how plants grow. So if you’re interested in gardening, give hydroponics a try and see the magic happen!

