Sustainable Solutions: Hydroponics and Sustainability
Hydroponics and sustainability go hand in hand when it comes to growing plants in a more efficient and eco-friendly way. With hydroponics, you can cultivate plants without soil, using nutrient-rich water instead. Sounds cool, doesn’t it? Well, it gets even better!
By adopting hydroponics, we can reduce water usage by up to 90% compared to traditional farming methods. That means less water waste and more sustainability for our precious planet. Plus, without the need for pesticides or herbicides, hydroponics promotes healthier and pesticide-free produce.
Not only does hydroponics provide a bountiful harvest, but it also enables us to grow food in urban areas, taking farm-to-table to a whole new level. So get ready to dive into the exciting world of hydroponics and sustainability, where plants thrive without soil and Mother Earth smiles along the way!
Hydroponics and Sustainability: Revolutionizing Farming for a Greener Future
Hydroponics and sustainability have become intertwined in the quest for a greener and more eco-friendly approach to farming. This innovative method of growing plants without soil has gained popularity in recent years, offering numerous benefits for both the environment and food production. In this article, we will delve into the world of hydroponics, explore its impact on sustainability, and uncover how this technology is revolutionizing the agricultural industry.
The Basics of Hydroponics: Growing Without Soil
Traditional farming methods rely on soil as a medium for plant growth, but hydroponics takes a different approach. With this method, plants are grown in nutrient-rich water solutions, allowing their roots to directly absorb the necessary nutrients. The absence of soil eliminates the risk of soil-borne diseases and pests, creating a cleaner and more controlled growing environment.
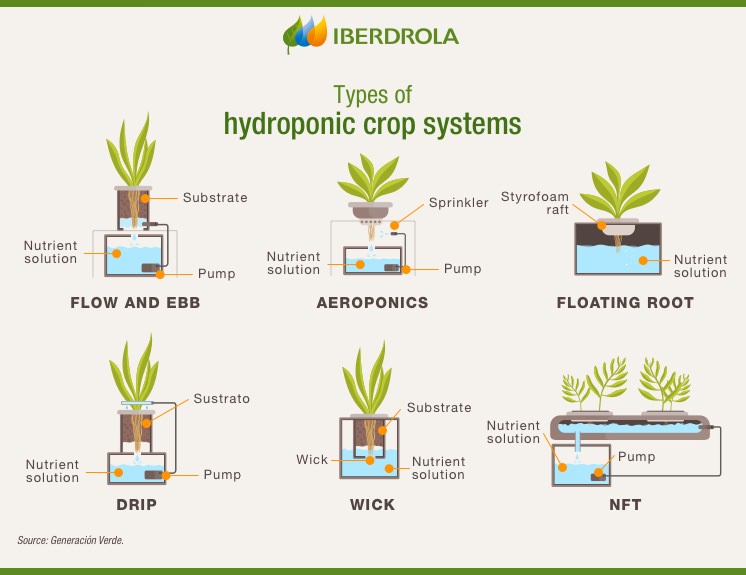
Hydroponics systems come in various forms, including deep water culture (DWC), nutrient film technique (NFT), and aeroponics. In DWC, plants are suspended in a water solution with the roots completely submerged. NFT systems use a shallow film of nutrient solution flowing over the roots. Aeroponics, on the other hand, involves suspending the roots in the air and misting them with a nutrient solution.
One of the key advantages of hydroponics is its ability to conserve water. Traditional farming methods often result in significant water loss due to evaporation and inefficient irrigation techniques. In contrast, hydroponics systems recirculate water, significantly reducing water usage while optimizing plant hydration.
The Impact on Sustainability: Environmental Benefits
Hydroponics offers a range of environmental benefits that contribute to sustainability efforts. First and foremost, this method minimizes the need for land, making it possible to grow crops in urban areas where space is limited. By utilizing vertical farming techniques, hydroponics maximizes land efficiency, potentially reducing deforestation and preserving natural habitats.
Additionally, hydroponics allows for precise control over nutrient delivery, optimizing plant growth and minimizing the use of fertilizers. Traditional farming often leads to nutrient runoff, which can pollute waterways and harm aquatic ecosystems. With hydroponics, the risk of nutrient pollution is significantly minimized, thus protecting local ecosystems and water quality.
Furthermore, hydroponics systems can be equipped with energy-efficient LED lights to provide artificial sunlight, enabling year-round cultivation. This reduces the need for extensive transportation and importation of out-of-season produce, ultimately lowering carbon emissions associated with long-distance food transport.
Hydroponics and Sustainable Food Production
In addition to its environmental benefits, hydroponics plays a crucial role in sustainable food production. By eliminating the dependence on soil and embracing efficient water and nutrient management, hydroponics ensures consistent crop yields and reduces the risk of crop failures due to adverse weather conditions. This method also allows for year-round cultivation, providing a more stable food supply regardless of seasonality.
Moreover, hydroponics enables the cultivation of crops in regions with challenging growing conditions, such as deserts or areas with poor soil quality. By utilizing controlled environments, farmers can produce high-quality, nutritious crops without relying on traditional agricultural practices that may deplete soil nutrients or contribute to soil erosion.
Additionally, hydroponics promotes local food production, reducing the carbon footprint associated with long-distance transportation. This method offers the potential for urban farming, allowing communities to grow their own food and ensuring access to fresh produce in urban areas where access to farmland is limited.
The Competitive Advantage: Hydroponics Vs Traditional Farming
While traditional soil-based farming has been the norm for centuries, hydroponics presents several distinct advantages over conventional agricultural methods. Here, we will compare these two approaches, showcasing how hydroponics brings sustainability to the forefront of food production:
Resource Efficiency: Hydroponics Takes the Lead
In terms of resource efficiency, hydroponics outshines traditional farming. By utilizing water recirculation systems, hydroponics minimizes water usage, reducing waste and conserving this precious resource. Traditional farming, on the other hand, often relies on wasteful irrigation methods that result in significant water loss due to evaporation and runoff.
Furthermore, hydroponics allows for better nutrient management. The precise control over nutrient delivery minimizes fertilizer usage, reducing the risk of nutrient pollution and the need for large-scale application of chemical fertilizers. Traditional farming, while often relying on excessive fertilizer use, runs the risk of nutrient runoff, leading to water pollution and ecological damage.
Overall, hydroponics sets a higher standard for resource efficiency, ensuring optimal water and nutrient management while minimizing waste and environmental impact.
Space Utilization: Hydroponics Transforms Urban Farming
When it comes to space utilization, hydroponics takes a leap forward compared to traditional farming. The ability to grow crops without the need for soil opens up new possibilities for urban farming in areas with limited available land. Vertical farming, a technique commonly utilized in hydroponics, maximizes land efficiency by stacking plants vertically, enabling multiple layers of cultivation in vertically stacked systems.
This vertical arrangement optimizes space utilization, making it possible to grow a large number of plants in a relatively small area. In contrast, traditional farming requires extensive land use, often resulting in deforestation as forests are cleared to make way for farmland. Hydroponics presents a sustainable alternative that minimizes land use and allows for food production in densely populated urban areas.
By transforming vacant buildings, rooftops, and unused urban spaces into thriving farms, hydroponics offers a solution for local food production, reducing the need for long-distance transportation and lowering carbon emissions associated with the importation of out-of-season produce.
The Future of Sustainable Agriculture: Hydroponics at the Forefront
As the world faces the challenges of climate change, resource scarcity, and a growing global population, sustainable agriculture is becoming more crucial than ever. Hydroponics has emerged as a beacon of hope, revolutionizing how we grow food and addressing the pressing need for environmentally friendly farming techniques.
With its ability to optimize resource efficiency, maximize space utilization, and provide year-round crop production, hydroponics offers a promising future for sustainable food production. By reducing the environmental impact of agriculture and ensuring a consistent food supply, hydroponics paves the way for a greener and more sustainable future.
As we continue to explore and embrace the potential of hydroponics, the benefits of this innovative farming method will likely extend beyond our imagination. From urban farming and local food production to reduced water usage and nutrient pollution, hydroponics holds the key to a sustainable and thriving agricultural industry.
Key Takeaways: Hydroponics and Sustainability
- Hydroponics is a method of growing plants without soil, using nutrient-rich water instead.
- By using hydroponics, we can save water as it requires less water compared to traditional farming methods.
- Hydroponics promotes sustainability by reducing the use of pesticides and herbicides.
- It allows us to grow crops in urban areas, reducing the need for long-distance transportation and decreasing carbon emissions.
- Implementing hydroponics can lead to more efficient land use, as it allows for vertical farming and utilizes smaller spaces.
Frequently Asked Questions
Welcome to our FAQ section on hydroponics and sustainability! In this section, we’ll address some common questions about the intersection of hydroponics and sustainability. Take a look at the questions below to deepen your understanding of this innovative gardening method and its impact on the environment.
1. How does hydroponics contribute to sustainability?
Hydroponics is a highly sustainable method of gardening because it minimizes the use of land, water, and inputs like pesticides and fertilizers. By growing plants without soil and in controlled nutrient-rich water environments, hydroponics eliminates the need for agricultural land. Additionally, hydroponics uses significantly less water compared to traditional soil farming, making it more sustainable in regions prone to drought. Furthermore, the controlled environment reduces the reliance on chemicals often required in conventional farming, resulting in a smaller environmental footprint.
Moreover, hydroponics can be practiced year-round, allowing for consistent food production regardless of seasonal limitations. This helps reduce the need for long-distance transportation and the associated carbon emissions. Overall, hydroponics offers a way to produce food sustainably with fewer resources and less impact on the environment compared to traditional farming methods.
2. Is hydroponics an energy-efficient method of gardening?
While hydroponics does require energy to operate the lighting, ventilation, and water circulation systems, it can still be an energy-efficient method of gardening. By utilizing energy-efficient LED lights and optimizing system design, it is possible to minimize energy consumption in hydroponic setups. Additionally, hydroponics allows for more precise control over the growing conditions, which can optimize plant growth and reduce energy waste.
Moreover, the controlled environment of hydroponics allows for the avoidance of environmental conditions that can be detrimental to plant health, such as extreme temperatures or pests. This reduces the need for energy-intensive climate control and pesticide applications. By leveraging technological advancements and mindful system design, hydroponics can overcome energy challenges, making it a sustainable choice for indoor food production.
3. Can hydroponics help conserve water resources?
Absolutely! Hydroponics is a water-efficient method of gardening that can help conserve this precious resource. Unlike traditional soil-based farming, hydroponics recirculates water, using up to 90% less water compared to soil farming. The plants’ roots are in direct contact with the nutrient-rich water, enabling them to efficiently uptake the water they need, while excess water is collected and recirculated. This closed-loop water system minimizes water waste and ensures optimal water usage.
In addition, hydroponic systems can be designed with water-saving features such as automated irrigation, water sensors, and water-efficient technologies like drip irrigation. These features ensure that water is used efficiently and that plants receive the necessary hydration without unnecessary wastage. Overall, hydroponics offers a sustainable solution to conserve water resources while producing high-quality crops.
4. What are the environmental benefits of hydroponic farming?
Hydroponic farming provides several environmental benefits. Firstly, it reduces the need for large areas of agricultural land, helping to protect natural habitats from conversion and preserving biodiversity. By growing plants hydroponically, it is also possible to minimize soil erosion and nutrient leaching, both of which can have detrimental effects on water quality and ecosystems.
Furthermore, hydroponics allows for precise nutrient delivery, preventing overuse of fertilizers that can lead to nutrient runoff, polluting water bodies. Additionally, since hydroponics eliminates the need for soil, it avoids soil degradation and contamination caused by excessive pesticide applications. By reducing chemical inputs and protecting the environment from soil pollution, hydroponic farming contributes to a healthier ecosystem.
5. Can hydroponics contribute to food security?
Hydroponics has the potential to contribute significantly to food security. By enabling year-round production and maximizing crop yield in minimal space, hydroponics offers a solution to overcome weather limitations and land scarcity. This method allows for consistent food production, irrespective of seasonal variations or challenging geographical conditions.
Moreover, hydroponics can be implemented in urban areas, reducing the reliance on long-distance transportation and ensuring local food production. By shortening the supply chain, it enhances food security by minimizing disruptions in food availability. Lastly, hydroponics offers the flexibility to grow a wide variety of crops, ensuring diversity in food production and enhancing nutritional outcomes for communities. By addressing the challenges of traditional farming, hydroponics presents a sustainable pathway towards global food security.

Hydroponics: A Sustainable Solution for the Future
Summary
Hydroponics is a sustainable farming method that doesn’t need soil. Instead, plants grow in nutrient-rich water. It saves water, uses less land, and reduces the need for harmful pesticides. This eco-friendly technique can even be done at home!
In hydroponics, water is recycled and reused, making it more water-efficient than traditional farming. It also allows for year-round production and can be done in urban areas. By growing plants without soil, hydroponics avoids soil erosion and contamination. It’s a cool way to grow food that helps the environment!

