Water World: Exploring Hydroponics and Aquaponics
In the world of innovative gardening, we have two fascinating methods: Hydroponics and Aquaponics. These are not your typical soil-based gardening techniques, but rather unique ways to grow plants using water as the primary medium.
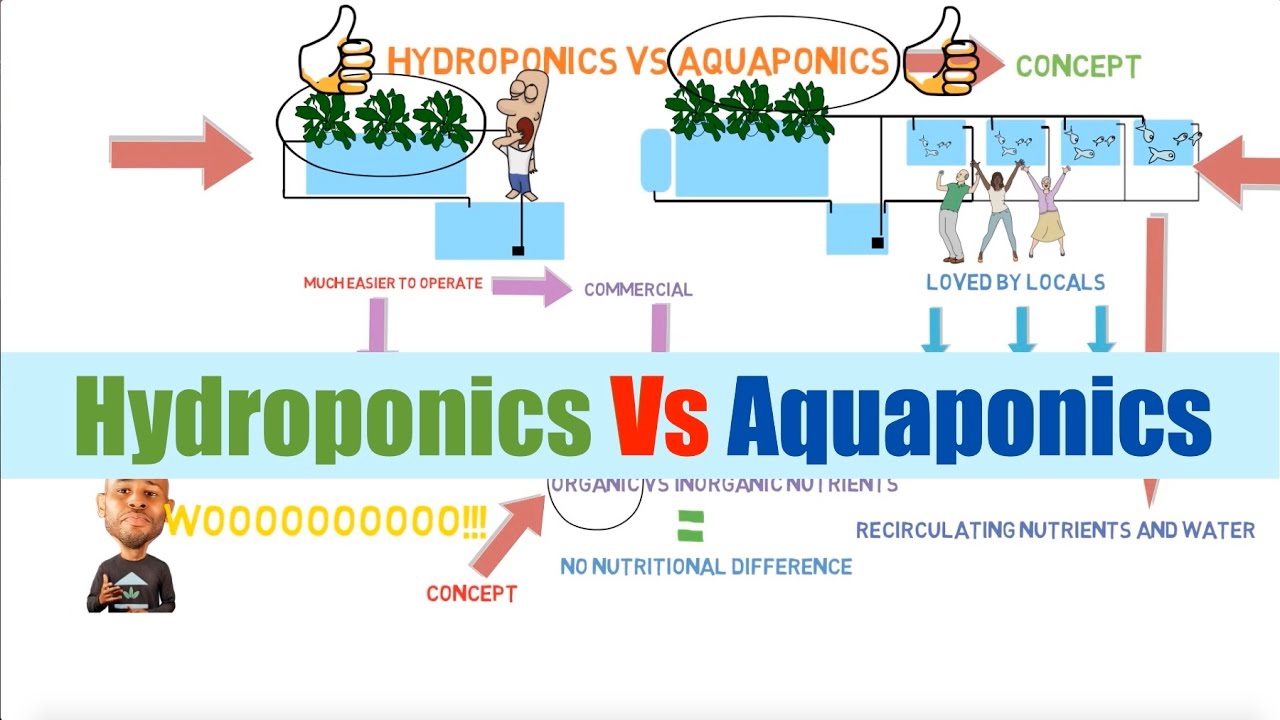
Hydroponics is a soil-less gardening method where plants are grown in a nutrient-rich water solution, providing them with everything they need to thrive. Aquaponics takes things a step further by combining hydroponics with fish farming. In this symbiotic system, fish waste provides the nutrients for the plants, while the plants filter the water for the fish.
These modern gardening methods offer numerous benefits, including efficient use of space and water, faster plant growth, and the ability to grow crops year-round. So, get ready to dive into the fascinating world of Hydroponics and Aquaponics, where plants flourish and fish and plants work together in harmony. Let’s explore the wonders of these soil-less gardening techniques together!
Hydroponics and Aquaponics: The Future of Sustainable Agriculture
Hydroponics and aquaponics are two revolutionary growing systems that are transforming the way we approach agriculture. These modern methods offer a more efficient and sustainable way to grow plants and produce food, without the need for soil or excessive water usage. In this article, we will delve into the world of hydroponics and aquaponics, exploring their benefits, differences, and how they are shaping the future of agriculture.
The Science Behind Hydroponics
Hydroponics is a soilless gardening method that allows plants to grow in a nutrient-rich water solution. By providing the plants with the necessary nutrients directly to their root systems, hydroponics optimizes plant growth and development. In a hydroponic system, plants are typically grown in containers filled with an inert growing medium like perlite or Rockwool. The water solution, containing the essential nutrients, is carefully monitored and supplied to the plants via a pump and timer system.
One of the key advantages of hydroponics is its ability to accelerate plant growth. Without the need to extract nutrients from soil, plants can focus their energy on growth and produce higher yields in a shorter time frame. Additionally, since hydroponics allows precise control over nutrient levels, pH, and water supply, plants can get exactly what they need, resulting in healthier and more productive crops.
The Benefits of Hydroponics
There are numerous benefits to utilizing hydroponic systems in agriculture. Firstly, hydroponics uses significantly less water compared to traditional soil-based farming methods. This is because water in a hydroponic system is recirculated and reused, minimizing waste and maximizing efficiency. In regions with limited water resources or in areas prone to droughts, hydroponics can provide a sustainable solution for food production.
Secondly, hydroponics eliminates the risk of soil-borne diseases and pests that can harm plants in traditional farming. By removing the need for soil, hydroponic plants are less susceptible to pathogens and pests, resulting in healthier crops. This also reduces the need for pesticides and chemical treatments, making hydroponics a more environmentally friendly approach to farming.
Lastly, hydroponics allows for year-round cultivation and can be practiced in urban areas where space is limited. Vertical hydroponic systems, such as tower gardens, make it possible to grow crops in small spaces, such as balconies or rooftops. This not only increases access to fresh produce in urban communities but also reduces the carbon footprint associated with transportation of food from rural areas to cities.
The Marriage of Fish and Plants: Aquaponics
Aquaponics takes hydroponics to the next level by integrating fish and plants in a symbiotic ecosystem. In an aquaponic system, fish waste provides the nutrients needed for plant growth, while the plants filter and purify the water for the fish. This natural cycle creates a sustainable and fully organic system that requires minimal external inputs.
The core of an aquaponic system is the fish tank, where aquatic animals, such as tilapia or trout, are housed. As the fish excrete waste, it accumulates in the water, creating ammonia. This ammonia is toxic to fish but serves as a valuable source of nitrogen for plants. The water from the fish tank is then pumped into hydroponic grow beds where the plants are cultivated. The plant roots naturally filter the water, removing the ammonia and other dissolved nutrients, thus creating a clean and oxygen-rich environment for the fish. The filtered water is then returned to the fish tank, completing the cycle.
The Advantages of Aquaponics
Aquaponics offers a range of advantages over traditional farming methods. Firstly, it is an incredibly efficient use of resources. By combining fish and plant cultivation, aquaponics utilizes the waste produced by the fish as a valuable source of nutrients for the plants. This eliminates the need for expensive synthetic fertilizers and significantly reduces water consumption compared to both hydroponics and conventional farming.
Aquaponics also allows for a more sustainable approach to food production. The symbiotic relationship between the fish and plants in an aquaponic system creates a closed-loop ecosystem where waste products are transformed into usable resources. This not only reduces waste but also eliminates the pollution and runoff associated with traditional agriculture.
Additionally, aquaponic systems can be tailored to fit various spaces and environments. From small-scale systems for home gardening to large commercial setups, aquaponics can be adapted to meet the needs of different growers. Its versatility and scalable nature make it a suitable option for both rural and urban environments, providing opportunities for local food production and reducing the carbon footprint associated with long-distance transportation.
Overall, hydroponics and aquaponics are revolutionizing the way we grow food. These sustainable methods offer a solution to the challenges faced by conventional agriculture, such as water scarcity, soil degradation, and pollution. By embracing these innovative techniques, we can create a more resilient and environmentally friendly food system for future generations. Whether you’re a home gardener looking to grow fresh produce or a large-scale farmer seeking efficient and sustainable methods, hydroponics and aquaponics provide a pathway to a greener and more productive future.
Key Takeaways: Hydroponics and Aquaponics
- Hydroponics is a soil-less gardening method that involves growing plants in nutrient-rich water.
- Aquaponics combines hydroponics and aquaculture, where fish waste provides nutrients to the plants.
- Both hydroponics and aquaponics allow plants to grow faster and use less water compared to traditional gardening methods.
- With hydroponics and aquaponics, you can grow fresh vegetables and herbs all year round.
- These sustainable farming methods are popular for their ability to produce high yields in small spaces.
Frequently Asked Questions
Welcome to our frequently asked questions section on Hydroponics and Aquaponics! Below, you’ll find answers to some common questions about these innovative methods of growing plants without soil. Whether you’re a beginner or just curious, this guide will help you grasp the basics and understand the benefits of these sustainable growing systems.
1. How does hydroponics work?
Hydroponics is a method of growing plants that eliminates the need for soil. Instead, plants are grown in a nutrient-rich water solution, with their roots suspended in this liquid. The water solution contains all the necessary nutrients that the plants need to grow, and an aerator is used to add oxygen to the water.
This setup allows for precise control over the growing environment, making it possible to optimize factors such as temperature, pH levels, and nutrient concentrations. By providing plants with an ideal growing environment, hydroponics can result in faster growth rates, higher yields, and the ability to grow plants in areas with limited access to arable land.
2. What is aquaponics and how does it work?
Aquaponics combines hydroponics with aquaculture, the practice of raising fish or aquatic animals in tanks or ponds. In an aquaponics system, fish waste provides the nutrients needed for plant growth. The waste, which would otherwise be considered a pollutant in aquaculture systems, is broken down by beneficial bacteria into nitrates, which are then absorbed by the plants as nutrients.
The plants, in turn, act as a natural filter, cleaning the water for the fish. This symbiotic relationship between the fish and plants creates a sustainable ecosystem where both thrive. Aquaponics is an environmentally friendly and efficient way to produce both fish and crops, minimizing water usage and reducing the need for chemical fertilizers.
3. What are the advantages of hydroponics and aquaponics?
Hydroponics and aquaponics offer several advantages compared to traditional soil-based agriculture. Firstly, these methods use significantly less water than conventional farming, making them more water-efficient. Secondly, since plants in hydroponics and aquaponics are grown in a controlled environment, they are less susceptible to pests and diseases, reducing the need for pesticides.
Another benefit is the ability to grow plants in areas with limited arable land, such as cities or deserts. Hydroponics and aquaponics also allow for year-round cultivation and can lead to higher yields and faster growth rates. Additionally, these methods minimize the need for synthetic fertilizers and promote sustainable food production practices.
4. What types of plants can be grown using hydroponics and aquaponics?
Virtually any plant that can be grown in soil can also be cultivated using hydroponics or aquaponics. Leafy greens, such as lettuce, spinach, and kale, are especially popular choices for hydroponic and aquaponic systems. Other plants that thrive in these systems include herbs like basil and cilantro, as well as vine crops like tomatoes and cucumbers.
By providing the necessary nutrients in a controlled environment, hydroponics and aquaponics can promote the healthy growth of a wide variety of plants, making them versatile options for growers.
5. What are the key challenges of hydroponics and aquaponics?
While hydroponics and aquaponics offer numerous benefits, they also come with their own set of challenges. One of the primary challenges is the initial setup cost, as hydroponic and aquaponic systems often require specialized equipment and infrastructure.
Another challenge is the need for continuous monitoring and maintenance of the systems to ensure optimal growing conditions. It’s essential to monitor factors such as pH levels, nutrient concentrations, and oxygen levels to avoid nutrient deficiencies or imbalances that could inhibit plant growth. Additionally, aquaponics requires careful management of the fish population to maintain a balanced ecosystem.

Hydroponics VS Aquaponics.. Here’s Which Ones REALLY Better!
Summary
Hydroponics and aquaponics are both cool ways to grow plants without using soil. In hydroponics, plants are grown in water with added nutrients, while aquaponics combines fish and plants in a symbiotic relationship. Hydroponics is great for small spaces and can help plants grow faster. Aquaponics is even cooler because it uses fish waste to feed the plants and the plants keep the water clean for the fish. Both methods are sustainable and can help us grow food in a more efficient and environmentally friendly way. So, whether you want to try hydroponics or aquaponics, give it a go and have fun growing your own food!

